- Published on
ArangoDB is underrated!
3 min read
- Authors
- Name
- Karan Pratap Singh
- @karan_6864

Table of Contents
Earlier this year, I started contributing to a social media centric project using React, Node, GraphQL, and ArangoDB....wait? what is that?
So what is ArangoDB?
ArangoDB is a highly available and scalable multi-model database to natively work with graphs, documents, and full text search in one database & query language.
ArangoDB is designed for fast development and easy scaling. The best part? It is opensource!!
What's a multi-model database?
A Multi-model database is a database that can store, index, and query data in more than one model. A model such as relational database, document-oriented database, graph database, key-value pairs.
For example, if your application requires a graph database and a key/value store (like redis), you would have to use second database technology to support it. Being multi-model, ArangoDB allows you to not only use one database for both but run ad-hoc queries on data stored in different models.
Hence, multi-model databases can provide an elegant solution to the challenge of managing heterogeneous data multi-model.
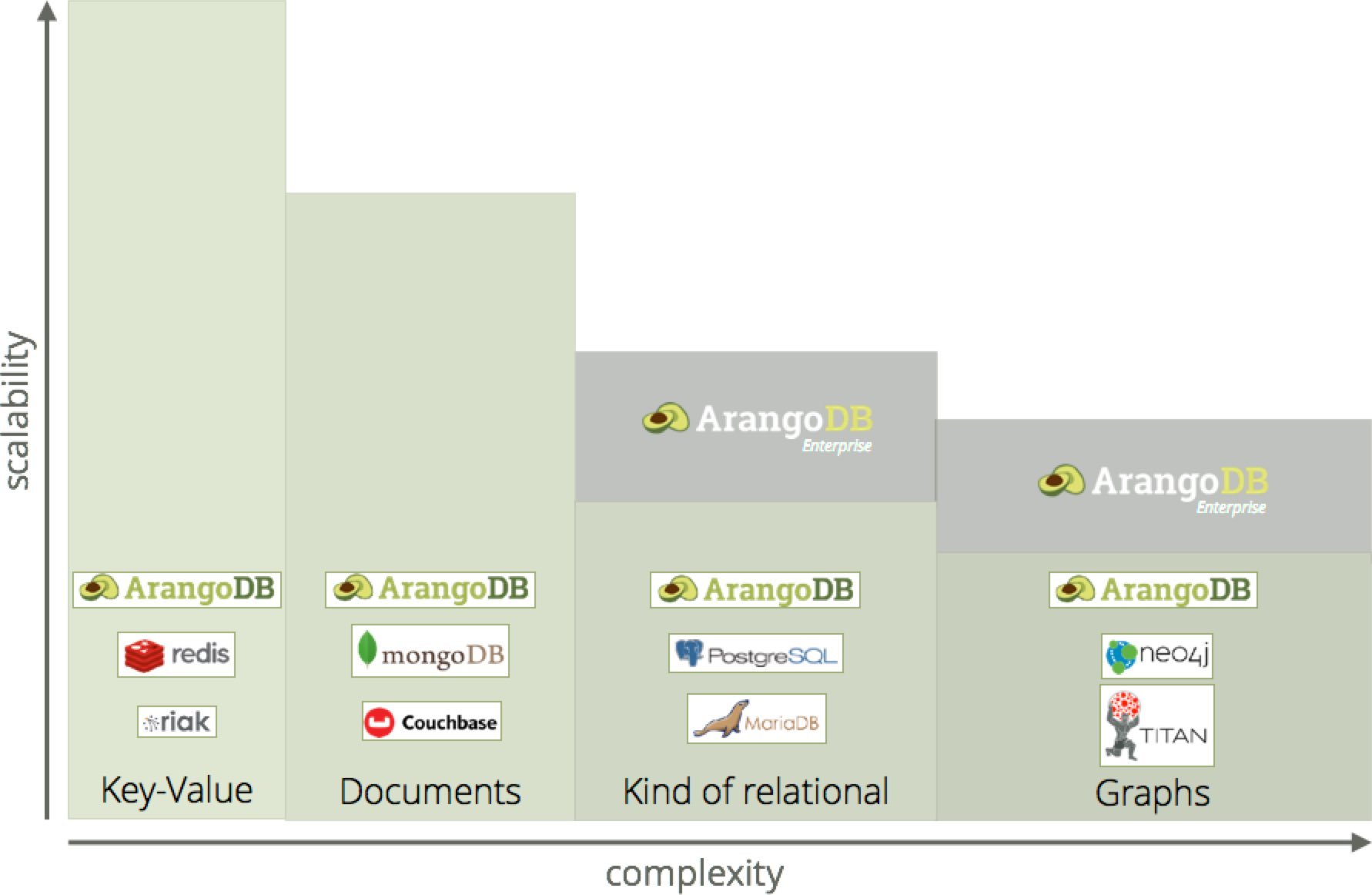 Here's how it compares to other databases
Here's how it compares to other databasesArangoDB vs Neo4J, ArangoDB vs MongoDB
AQL is powerful
The ArangoDB Query Language (AQL) is a declarative language, meaning that a query expresses what result should be achieved but not how it should be achieved. It's quite human readable as well.
Here's a basic example with AQL
-- Inserting a document
INSERT {
"name": "Karan",
"role": "Full Stack Developer",
"age": 21
} INTO Users
-- Reading documents
FOR user IN Users
RETURN user
-- Reading documents with filter
FOR user IN Users
FILTER user.name == "Karan"
RETURN user
-- Reading specific document
RETURN DOCUMENT("Users", "<document-key>")
Read more about basic operations here
This is just scratching the surface of AQL. Some of the other great features are powerful graphql traversals, array operators, high-level functions for geo index based searches.
Example for a simple graph traversal
-- General syntax
[WITH vertexCollection1[, vertexCollection2]]
FOR vertex[, edge[, path]]
IN [min[..max]]
OUTBOUND|INBOUND|ANY startVertex
RETURN vertex[, edge[, path]]
-- Example with Users collection
WITH Users
FOR vertex, edge, path IN 1..1 OUTBOUND "users/document-key"
RETURN vertex
ArangoDB Oasis
Oasis is a fully managed cloud offering by Arango which makes it easier than ever to scale your cluster. No more worrying about AWS EC2 instances!!
Personal experience
I found ArangoDB to be a delight, it's powerful graph traversals and flexibility of AQL helped with a lot of complicated features we were working on. Hopefully, many more people give this database a try.